Fill a Valid Prescription Pad Template
The Prescription Pad form serves as a critical tool in the healthcare landscape, facilitating the safe and effective dispensing of medications. This form is not merely a piece of paper; it embodies a complex interaction between healthcare providers, patients, and pharmacists. Essential components of the form include patient identification details, the prescribing physician's information, and a comprehensive list of medications prescribed, complete with dosages and instructions for use. Moreover, the form often includes sections for refills and the duration of the prescription, ensuring that patients receive their medications in a timely manner. Additionally, legal and regulatory requirements play a significant role in shaping how this form is utilized, as it must comply with state and federal laws to prevent misuse and ensure patient safety. Understanding the intricacies of the Prescription Pad form is vital for all stakeholders involved, as it not only streamlines the medication management process but also safeguards public health.
Document Details
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
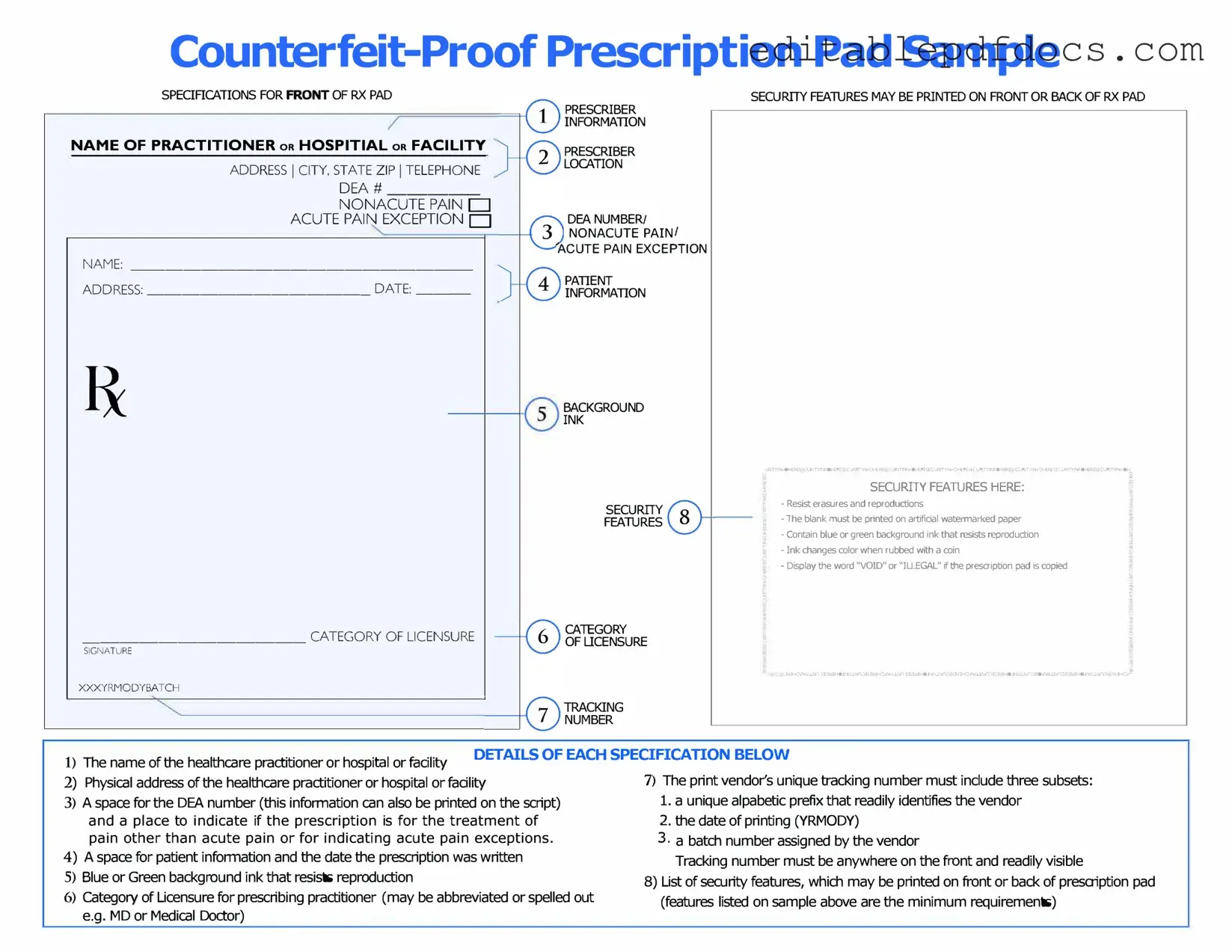
| Purpose | The Prescription Pad is used by healthcare providers to prescribe medications to patients. |
| Format | Typically, the form includes fields for patient information, medication details, dosage, and prescribing provider's information. |
| Legal Requirement | In many states, using a standardized prescription pad is required by law to ensure patient safety and reduce prescription fraud. |
| State-Specific Forms | Each state may have its own version of the Prescription Pad, governed by state laws such as the Controlled Substances Act. |
| Security Features | Prescription Pads often include security features like watermarks or unique serial numbers to prevent counterfeiting. |
| Electronic Prescriptions | Many healthcare providers now use electronic prescription systems, which are often considered more secure and efficient. |
| Record Keeping | Providers must keep records of all prescriptions issued, as required by state regulations. |
| Patient Information | Prescriptions must include accurate patient details to ensure the correct medication is dispensed. |
| Expiration Dates | Prescriptions typically have an expiration date, after which they are no longer valid for dispensing. |
| Controlled Substances | Prescribing controlled substances requires additional documentation and adherence to stricter regulations. |
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out a Prescription Pad form, attention to detail is crucial. Here are six important guidelines to keep in mind:
- Do ensure all patient information is accurate and complete.
- Don't leave any sections blank; incomplete forms can lead to delays in treatment.
- Do clearly write the medication name, dosage, and instructions.
- Don't use abbreviations that could be misunderstood; clarity is essential.
- Do sign and date the form to validate the prescription.
- Don't forget to check for any potential drug interactions before prescribing.
Following these guidelines will help ensure that the prescription process goes smoothly and safely for everyone involved.
Documents used along the form
The Prescription Pad form is a crucial document in the healthcare process, primarily used by healthcare providers to prescribe medications to patients. Alongside this form, several other documents play important roles in ensuring proper patient care and medication management. Here are some commonly used forms and documents that often accompany the Prescription Pad.
- Patient Information Form: This document collects essential details about the patient, including personal information, medical history, and allergies. It ensures that healthcare providers have a comprehensive understanding of the patient's health status.
- Medication Administration Record (MAR): This form tracks all medications administered to a patient. It includes details such as dosage, administration times, and the healthcare professional responsible for giving the medication.
- Chick-fil-A Job Application: Completing the application accurately can significantly improve your chances of landing a job at this renowned fast-food chain. For an easier process, consider using Fillable Forms that simplify the application experience.
- Informed Consent Form: Before prescribing certain medications or treatments, providers may require patients to sign this form. It confirms that the patient understands the risks, benefits, and alternatives associated with the treatment.
- Referral Form: When a healthcare provider needs to send a patient to a specialist, this form is used. It includes the patient's information and the reason for the referral, ensuring continuity of care.
- Insurance Authorization Form: This document is often necessary for obtaining approval from an insurance company before certain medications or treatments can be prescribed. It helps ensure that the costs will be covered.
- Follow-Up Appointment Reminder: After a prescription is issued, a follow-up appointment may be necessary. This reminder form helps patients keep track of their next visit, ensuring ongoing care and monitoring of their condition.
Each of these documents serves a specific purpose in the healthcare process, contributing to effective communication and patient safety. Together, they create a comprehensive framework that supports both providers and patients in managing health and treatment plans.
Popular PDF Forms
Wage and Tax Statement - Failure to receive a W-2 can lead to complications in filing taxes.
Understanding the intricacies of the Room Rental Agreement requirements is vital for both landlords and tenants to establish clear expectations and mitigate potential disputes during the rental period.
How to Fill Out Pdf on Phone - This Employment Application form is usually required for all job vacancies within an organization.
Similar forms
Patient Information Form: This document collects essential details about the patient, such as name, address, and medical history, similar to how a Prescription Pad captures patient data for medication purposes.
Medication Administration Record (MAR): The MAR tracks medications administered to patients, providing a record of dosages and administration times, akin to the documentation of prescribed medications on a Prescription Pad.
Referral Form: This form is used to refer patients to specialists, containing patient information and reason for referral, similar to how a Prescription Pad may indicate a need for further medical intervention.
Informed Consent Form: Patients sign this document to acknowledge understanding of treatment risks and benefits. Like the Prescription Pad, it is a critical part of the medical record.
Medical History Form: This document gathers comprehensive background information about a patient’s past health issues, similar to the context provided in a Prescription Pad for effective medication management.
Discharge Summary: This summary provides an overview of a patient's hospital stay and ongoing care needs, which can include medication plans, paralleling the information recorded on a Prescription Pad.
Insurance Authorization Form: This document is necessary for obtaining approval for medical services. It shares similarities with the Prescription Pad in that both are used to facilitate patient care and treatment.
-
New York DTF-84 Form: This form is essential for individuals requiring access to their state tax records in New York. Similar to other important documents, it enables authorized parties to obtain specific tax information. For more details, visit https://nyforms.com/new-york-dtf-84-template.
Lab Requisition Form: This form is used to request laboratory tests for patients. It is similar to the Prescription Pad in that it serves as a formal request for medical services.
Progress Note: Healthcare providers use progress notes to document patient visits and treatment plans, much like how a Prescription Pad records medication instructions and patient care details.
Treatment Plan: This document outlines the proposed course of treatment for a patient, including medications. It parallels the Prescription Pad by detailing the therapeutic approach for a patient’s condition.
Common mistakes
Filling out a Prescription Pad form is a crucial task that requires attention to detail. Mistakes can lead to confusion, delays, and even serious health risks for patients. One common error occurs when the prescriber fails to include the patient's full name. Omitting this vital information can result in the wrong individual receiving medication, which can have dire consequences.
Another frequent mistake is neglecting to specify the dosage of the medication. Prescribers may assume that the pharmacy will know the appropriate amount, but this can lead to misunderstandings. Clear dosage instructions are essential to ensure that patients take their medications safely and effectively.
Inaccurate or incomplete medication names can also pose significant problems. Sometimes, a prescriber might use a shorthand or an abbreviation that is not widely recognized. This can confuse pharmacists and potentially delay treatment. It is always best to write out the full name of the medication to avoid any ambiguity.
Failing to indicate the frequency of administration is another common oversight. A prescription that does not specify how often a patient should take their medication can lead to improper use. Patients might take too much or too little, which can diminish the effectiveness of the treatment or cause adverse effects.
Additionally, prescribers sometimes forget to include the date on the Prescription Pad form. This detail is not merely a formality; it helps pharmacies track the validity of the prescription. An undated prescription may raise questions about its legitimacy and could lead to complications in filling it.
Another mistake involves not providing a clear indication of whether the prescription is for a refill. Patients often rely on refills for chronic conditions, and failing to specify this can disrupt their treatment regimen. Clear communication about refills is essential for ongoing patient care.
Prescribers may also overlook the importance of their own signature. A prescription without a signature is invalid and cannot be filled. This simple yet crucial step is often forgotten in the rush of a busy practice.
Another error arises when prescribers do not verify the patient's allergies or existing medications. This oversight can lead to dangerous drug interactions. A thorough review of the patient's medical history should always precede prescribing new medications.
In some instances, prescribers might use outdated or incorrect forms. Using an old version of the Prescription Pad can lead to confusion, as pharmacies may not accept it. Always ensuring that the most current form is used can prevent unnecessary complications.
Lastly, failing to communicate clearly with patients about their prescriptions can result in misunderstandings. Patients should leave the office with a thorough understanding of their medication, including how to take it and any potential side effects. Clear dialogue can enhance patient safety and adherence to treatment plans.